Where Ladino and Yiddish is spoken
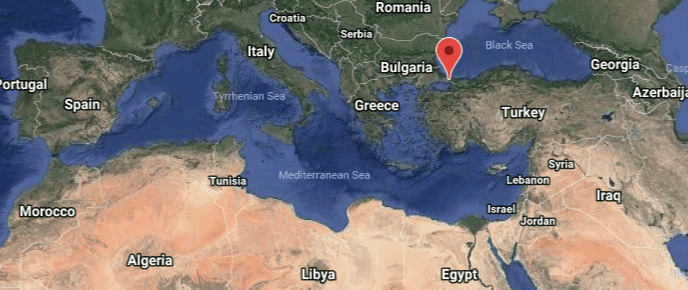 Where Ladino was/is spoken
Where Ladino was/is spoken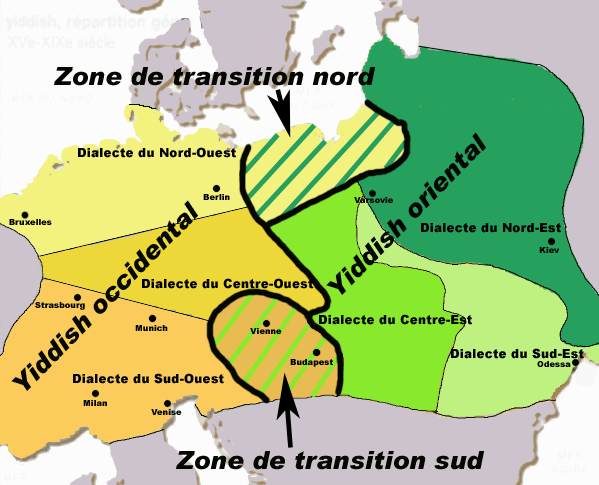 Where Yiddish was spoken
Where Yiddish was spoken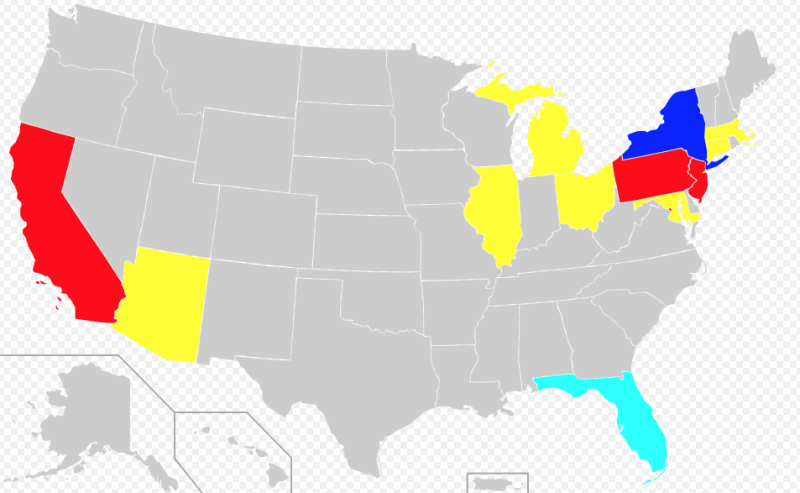 Where Yiddish is spoken in the USA
Where Yiddish is spoken in the USA Legend
Legend
Ladino, also called Judeo-Spanish, Sefardí, Judío/Djudyo, and Haquetía, among others, is a Jewish language of Latin origin, spoken primarily in Bosnia and Herzegovina, Greece, France, Turkey, and Israel.
Ladino has its roots in the Latin spoken by the Romans who occupied the Iberian Peninsula from 200 B.C.E. to 425 B.C.E., but today’s Ladino is closer to modern Spanish plus a mix of whatever other languages Ladino speakers knew.
How many people still speak Ladino? Most estimates say that between 160,000 and 300,000 Sephardim (Jews of Middle Eastern or Spanish origin) worldwide have some knowledge of Ladino. In Israel, the estimate is that 50,000 to 80,000 people are somewhat familiar with Ladino.
For centuries, Ladino was written in Hebrew characters, using either the special alphabet employed by the medieval commentator Rashi or a cursive script called solitreo. Most Ladino literature is written in the Rashi alphabet. Today, Ladino is written in Latin alphabet, but in phonetic transcription instead of the spelling system of today’s Spanish.
>Man speaking Ladino
How many Yiddish speakers are there today?
In the years before the Second World War, there were probably 10-11 million Yiddish speakers worldwide. As a result of the Holocaust, cultural assimilation in America and in the USSR, and shift to Hebrew in Israel, today there an estimated 3 million speakers left, most of whom no longer use Yiddish as their primary language.
What language is closest to Yiddish?
Of all the German dialects Yiddish is probably closest to some forms of Badisch and Swiss German. Yiddish was the language of Eastern European (Ashkenazi) Jews until the Holocaust and is now primarily spoken in Hasidic communities in Israel, the USA, England, Australia, Canada and Belgium.
Where is the Yiddish language from?
Yiddish was invented by Jews who had arrived in Europe with the Roman army as traders, later settling in the Rhineland of western Germany and northern France. Mixing Hebrew, Aramaic and Romance with German, they produced a unique language, not just a dialect of German.
What's the difference between Yiddish and Hebrew?
Hebrew in its modern form is spoken by many of the seven million people in Israel. Yiddish (ייִדיש yidish or אידיש idish, literally "Jewish") is a High German language of Ashkenazi Jewish origin, spoken throughout the world. It developed as a fusion of German dialects with Hebrew, Aramaic, Slavic languages.
What alphabet is used in Yiddish?
Yiddish orthography is the writing system used for the Yiddish language. It includes Yiddish spelling rules and the Hebrew script, which is used as the basis of a full vocalic alphabet. Letters that are silent or glottal stops in the Hebrew language are used as vowels in Yiddish. More . . .
>Yiddish and German side by side
>Man speaking Yiddish
After the Jews were exiled by the Romans from their homeland in Israel following the destruction of the Second Temple in 70 AD, the far flung Jewish communities invented new languages called Ladino and Yiddish. These languages allowed Jews to speak to other Jews living in another country. A Jewish person, for example, living in Paris, France easily spoke Yiddish to someone living in Moscow, Russia without each having knowledge of French and Russian.
